Herpes genital infection is a common sexually transmitted infection caused by the herpes
simplex virus (HSV). This viral infection affects millions of people worldwide and can cause
a variety of symptoms that can impact a person’s physical and emotional well-being.
Understanding the symptoms, early diagnosis, and treatment options for herpes genital
infection is crucial in effectively managing the condition and preventing its spread.
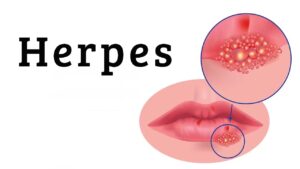
Symptoms of Genital Herpes Infection:
Genital herpes infection can cause a range of symptoms that vary from person to person.
The most common symptoms of herpes genital infection include:
1. Painful Sores or Blisters: One of the primary symptoms of genital herpes is the
presence of painful sores or blisters around the genital area. These sores can be
filled with fluid, and they can appear on the genitals, buttocks, or thighs. The sores
can be tender, itchy, and can cause discomfort during activities such as urination.
2. Flu-Like Symptoms: Some individuals with genital herpes may experience flu-like
symptoms, including fever, headache, muscle aches, and swollen lymph nodes in
the groin area. These symptoms may occur before or during an outbreak of genital
herpes sores.
3. Itching or Tingling Sensations: Before the appearance of sores or blisters, some
individuals may experience itching, tingling, or burning sensations in the genital
region. These sensations are often an early sign of an impending herpes outbreak.
4. Pain or Burning Sensation During Urination: The presence of genital herpes sores
can cause pain or a burning sensation when urinating. This discomfort can make it
challenging for individuals to urinate comfortably during an outbreak.
Early Diagnosis of Genital Herpes:
Diagnosing genital herpes early is essential for initiating prompt treatment and managing
the symptoms effectively. Healthcare providers can diagnose genital herpes through a
combination of physical examination, symptom evaluation, and laboratory tests. Some
common diagnostic methods for genital herpes include:
1. Visual Examination: Healthcare providers can visually inspect the genital area for
the presence of sores, blisters, or other signs of herpes infection. A physical
examination can help healthcare providers assess the severity and location of the
infection.
2. Swab Test: During an active outbreak of herpes sores, healthcare providers may take
a swab sample from the affected area to test for the presence of the herpes simplex
virus. This test can help confirm the diagnosis of genital herpes.
3. Blood Tests: Blood tests can detect the presence of herpes simplex virus antibodies
in the bloodstream. These tests can indicate whether an individual has been
exposed to HSV-1 or HSV-2 and can help diagnose genital herpes, even in the
absence of active symptoms.
Treatment Options for Genital Herpes:
While there is currently no cure for genital herpes, various treatment options are available
to help manage the symptoms and reduce the frequency and severity of outbreaks.
Common treatment approaches for genital herpes include:
1. Antiviral Medications: Antiviral medications are the primary treatment for genital
herpes infection. These medications, such as acyclovir, valacyclovir, and
famciclovir, work by suppressing the replication of the herpes virus and reducing the
duration and intensity of outbreaks. Antiviral medications can be taken orally or
applied topically to the affected area.
2. Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or
acetaminophen, can help alleviate discomfort and pain associated with genital
herpes sores. Topical pain-relieving creams or ointments may also provide relief
from itching and tenderness.
3. Lifestyle Modifications: Making lifestyle changes can help manage genital herpes
symptoms and reduce the risk of outbreaks. Practicing good hygiene, avoiding
sexual activity during outbreaks, using condoms, and managing stress through
relaxation techniques and regular exercise can all contribute to managing genital
herpes effectively.
4. Supportive Care: Seeking emotional support and guidance from healthcare
professionals, support groups, or counselors can help individuals cope with the
emotional and psychological aspects of living with genital herpes. Open
communication with sexual partners about the infection and practicing safe sex can
also reduce the risk of transmitting the virus to others.
In conclusion, herpes genital infection is a common and manageable condition that can
cause discomfort and emotional distress. Recognizing the symptoms, seeking early
diagnosis, and following appropriate treatment can help individuals effectively manage
genital herpes and improve their quality of life. By staying informed, seeking medical
guidance, and adopting healthy lifestyle practices, individuals can navigate the challenges
of living with genital herpes and maintain their overall well-being.